by Kristen Minogue
Tidal marshes have long been lauded as carbon sinks for their ability to pull CO2 from the atmosphere and bury it in the soil, what scientists have taken to calling “blue carbon.” But wetlands are also notorious methane emitters. Now ecologists suspect that only a select few wetland types can reliably act as sinks, and that number may shrink as sea levels rise.

The Kirkpatrick Marsh on SERC's campus in Edgewater, MD. Tidal wetlands both store and release greenhouse gases. Which will prevail as the planet warms is a question ecologists are still trying to answer. (Credit: Gary Peresta/SERC)
It all comes down to what’s in the soil, according to SERC ecologist Pat Megonigal. The various microbes that battle for dominance beneath the surface can determine whether a wetland ultimately becomes a greenhouse gas sink or a greenhouse gas source. Some microbes in tidal marshes – the sulfate-reducers – get their energy by respiring or “breathing” sulfur oxides in sea water, a relatively harmless process as far as the atmosphere is concerned. Others – the methanogens – break down CO2 and re-emit it as methane. If the sulfate-reducers win, the wetland remains a sink. If the methanogens win, it turns into a source.
Megonigal and his colleagues Hanna Poffenbarger and Brian Needelman of the University of Maryland discovered that the salinity of the water flooding marsh soils may tip the scale one way or the other. Sea water is spiked with high concentrations of sulfate (SO4), enabling the sulfate-reducing microbes to outcompete the methanogens. But in freshwater marshes, methanogens have more of an edge. After looking at data from 31 different marshes, some from previous studies and some from unpublished measurements in SERC’s own tidal marsh, Megonigal and his team found what could be the critical salinity for a marsh to go from a greenhouse gas source to a sink: 18 parts per thousand, or about half as salty as sea water.
While there were some less salty marshes that could act as sinks, the data varied too widely to make reliable predictions. Only when salinity reached 18 parts per thousand could the researchers be 95 percent confident the marsh would benefit climate – meaning the methane the marsh emitted was less powerful than the CO2 it absorbed. Unfortunately, says Megonigal, this number rules out most marshes in Chesapeake Bay.
But there’s another catch. As sea level rises, the marshes could start to emit even more methane. That’s because if the water table is too high, the soil becomes anaerobic, smothering out the oxygen that could help break down the methane.

SERC intern Lillian Aoki examines a gas sample from marsh plants in a closed chamber to calculate how much methane they are emitting. (Credit: Thomas Mozdzer/SERC)
While working on the SERC marsh with Megonigal’s lab this summer, interns Shannon Hagerty and Lillian Aoki found that a rising water table could make marshes emit more methane from their soils. They simulated sea level rise by filling cylindrical columns with dirt and plants from the marsh and placing them at various elevations in the water, ranging from 35 cm higher to 10 cm lower than current sea level. Then they measured which cylinders emitted the most methane.
Hagerty’s preliminary findings suggested the cylinders submerged the most – the ones mimicking conditions if sea level rose 10 cm – emitted roughly nine to 12 times as much methane as the higher, drier cylinders.
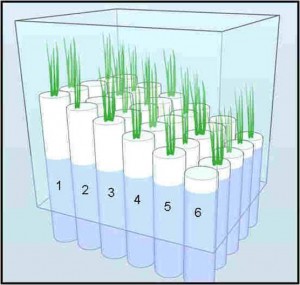
Scientists use these cylindrical marsh organs to simulate higher sea levels. The white cylinders are submerged at different depths in the water. The plants submerged deepest (row 6) experience the highest sea levels. The plants elevated highest (row 1) experience the lowest sea levels. (Credit: Adam Langley/SERC)
Combined, these influences suggest that creating or restoring the saltiest wetlands has promise as a way of absorbing greenhouse gases, provided they continue to sit well above sea level. But as the oceans continue to rise, if the saltier marshes can’t keep up, those marshes would also be the first to drown and disappear.


Pat-
I love the work. I was just checking up on you, seeing what the old lab was up to! It looks like you guys are busy! Talk to you soon.
Sara